Algorithm:
We are given a series
Evaluate
improper integral
![]() .
The conclusion (whether it converges or not) also applies to the series
.
The conclusion (whether it converges or not) also applies to the series
The Integral test is used as follows.
Algorithm:
We are given a series∑ ak with positive terms. Assume that the terms ak are given by an expression that also defines some positive and non-increasing functionf (x) on some interval[K,∞).
Evaluate improper integral. The conclusion (whether it converges or not) also applies to the series
∑ ak.
One also gets an estimate, see Integral test in Theory - Testing convergence.
When is this test useful? If we look at the given series and like the idea of integrating instead of summing, then this test is the obvious choice - of course assuming that the function in question is non-increasing.
Example: Decide on convergence of the series
![]()
Since the function
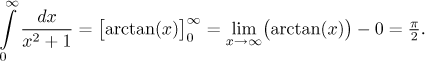
Since this integral converges, by the Integral test also the given series converges.
For other examples see this problem and this problem in Solved Problems - Testing convergence.