Example: Decide whether the following integral converges:
![]()
Solution:
We check that there is just one problem, the lower limit leads to zero in the
denominator. Therefore we have an improper integral of the basic type and we
can apply convergence tests. First we try to apply the easier Comparison
Test. Note that the given function is negative on the integration interval,
therefore we have to use the absolute value. For
![]()
We obtained a reasonable inequality, so it is time to check on the test
integral. This is easy, we remember the powers scale and therefore we know
that
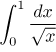 converges (check that this integral is equal to 2). Consequently, since
the given integral is supposed to be smaller, it must be also convergent (and
its absolute value cannot exceed 2).
converges (check that this integral is equal to 2). Consequently, since
the given integral is supposed to be smaller, it must be also convergent (and
its absolute value cannot exceed 2).
We were lucky and the problem could be solved easily using the Comparison
Test. To get some practice, we will now try to use the Limit Comparison test.
First we will determine the best test function by ignoring parts of f
that are not equal to zero when
![]()
This guess has to be justified:
![]()
So the functions are indeed about the same near the problem point 0 (from the
right). Since the test integral
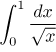 converges, by the Limit Comparison test, the given integral also converges.
converges, by the Limit Comparison test, the given integral also converges.