Problem: We have two quantities, f and g, both depend on time. We want to find some relationship between their derivatives by t.
Solution:
Step 1. Find some relationship between f and g, usually
in the form of
Step 2. Differentiate this relationship, using the chain rule on the
right.
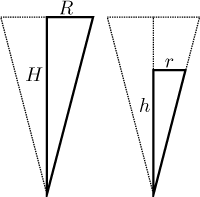
Example: A glass for wine has the shape of a regular cone with height
Solution: There are two quantities that change, the volume of wine in
the glass V and the level of wine h. The cone has parameters
We want to know the rate of change of h. First we need a relationship between V and h, but volume depends on height and radius. To calculate radius based on height we use similarity of triangles.

From this we know that
![]()
We differentiate by t on both sides, keeping in mind that r is also a function of t. We use the Leibniz notation as it seems better suited to this kind of work.
![]()
From this we get
![]()
We have an expression for the rate of change of the level of wine, it remains
to substitute the given data, in particular
For more insight and another example see Related rates in Theory - Applications, see also Solved Problems - Applications.
Global extrema, optimization
Back to Methods Survey -
Applications