Algorithm:
We are given a series
![]() ak
ak
Step 1. Evaluate the limit
![]()
Step 2. Assume that this limit exists.
• If
• If
The Root test is used as follows.
Algorithm:
We are given a serieswith non-negative terms. ak
Step 1. Evaluate the limit
Step 2. Assume that this limit exists.
• Ifϱ < 1, then the given series converges.
• Ifϱ > 1, then the given series diverges.
This test is obviously perfect for series whose term are of the form
If p(x) is a non-zero polynomial, then
Note, however, that the case
Example: Decide on convergence of the series
![]()
The denominator just calls for the Root test. Using the fact above we get
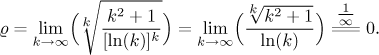
Since
For other examples see especially this problem, this problem, and this problem in Solved Problems - Testing convergence.
Sometimes one has to use more general (and less convenient) versions of the Root test, see Root and Ratio test in Theory - Testing convergence; for an example see this problem in Solved Problems - Testing convergence, also look at this problem.
One can also use this test to get some information about series with general terms, not just non-negative, see the Note at the end of the section Root and Ratio test in Theory - Testing convergence.